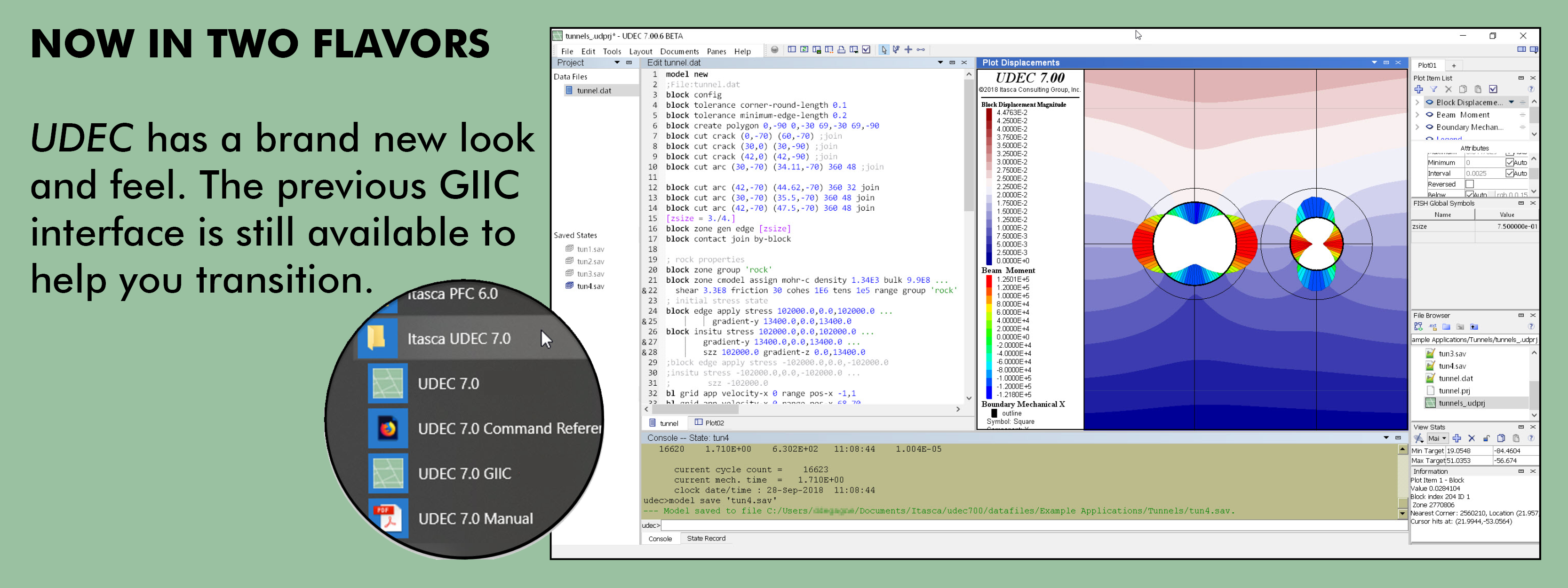
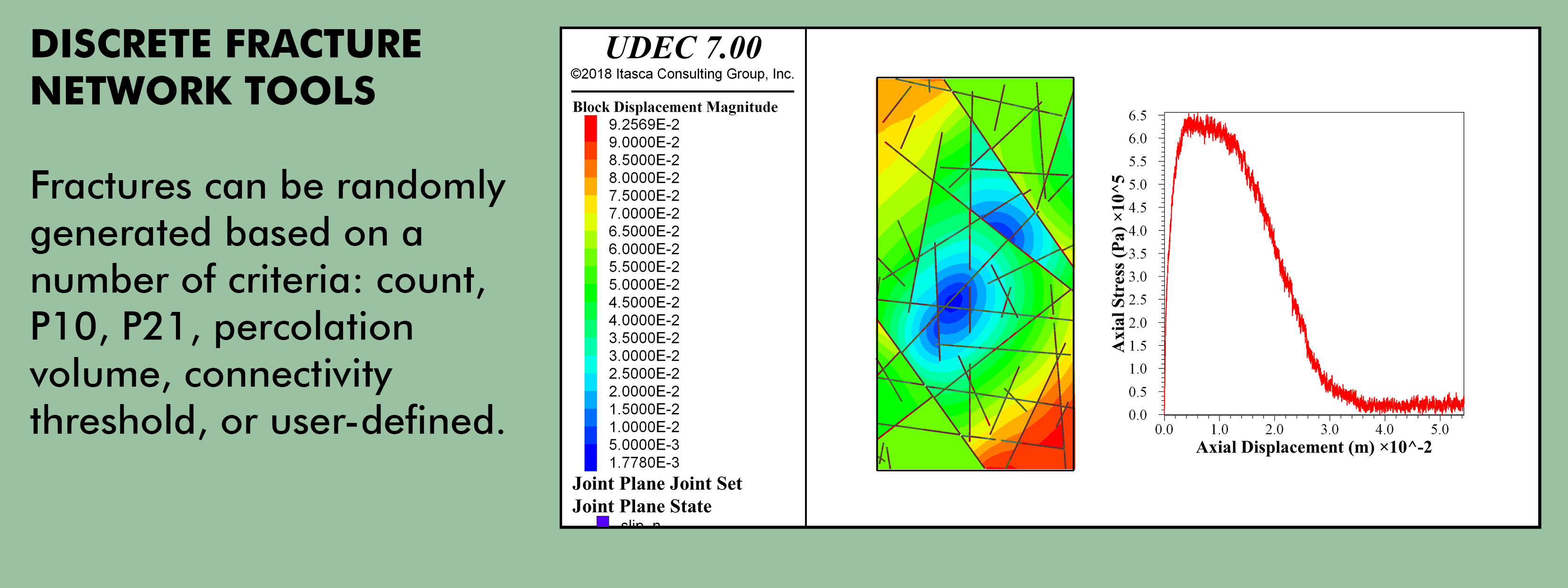
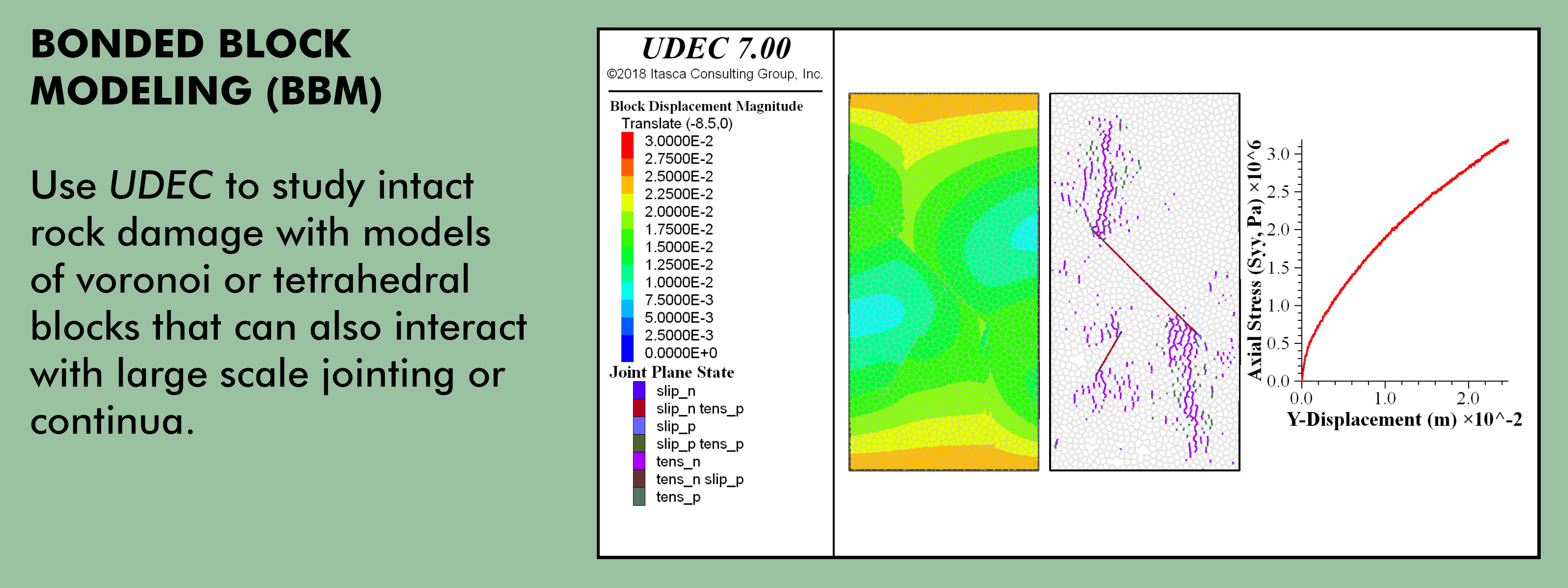
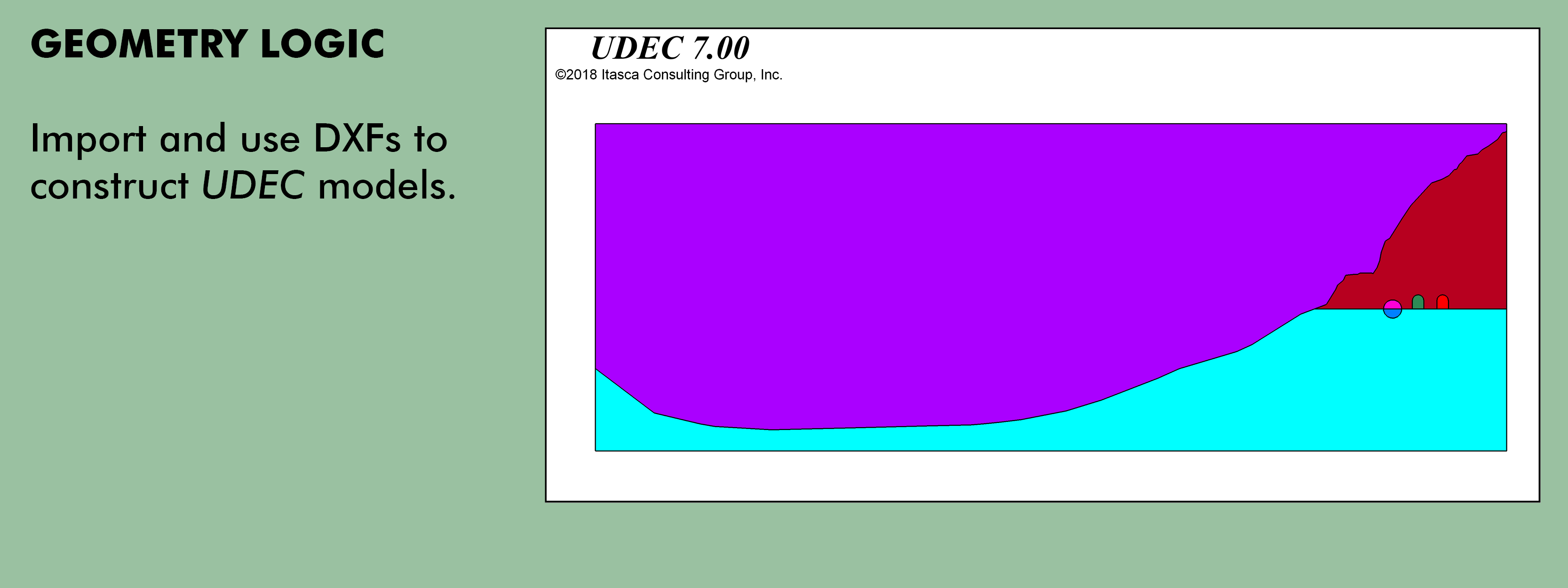
Description
The Universal Distinct Element Code (UDEC) is a two-dimensional numerical program that simulates the quasi-static or dynamic response to loading of media containing multiple intersecting joint structures.
The discontinuous medium is represented as an assemblage of discrete blocks while the discontinuities are treated as boundary conditions between blocks. Large displacements along discontinuities and rotations of blocks can occur. UDEC utilizes an explicit solution scheme that can model complex, nonlinear behaviors.
Models may contain a mix of rigid or deformable blocks. Deformable blocks are defined by a continuum mesh of finite-difference zones, with each zone behaving according to a prescribed linear or nonlinear stress-strain law. The relative motion of the discontinuities is also governed by linear or nonlinear force-displacement relations for movement in both the normal and shear directions. Joint models and properties can be assigned separately to individual, or sets of, discontinuities.
Applications
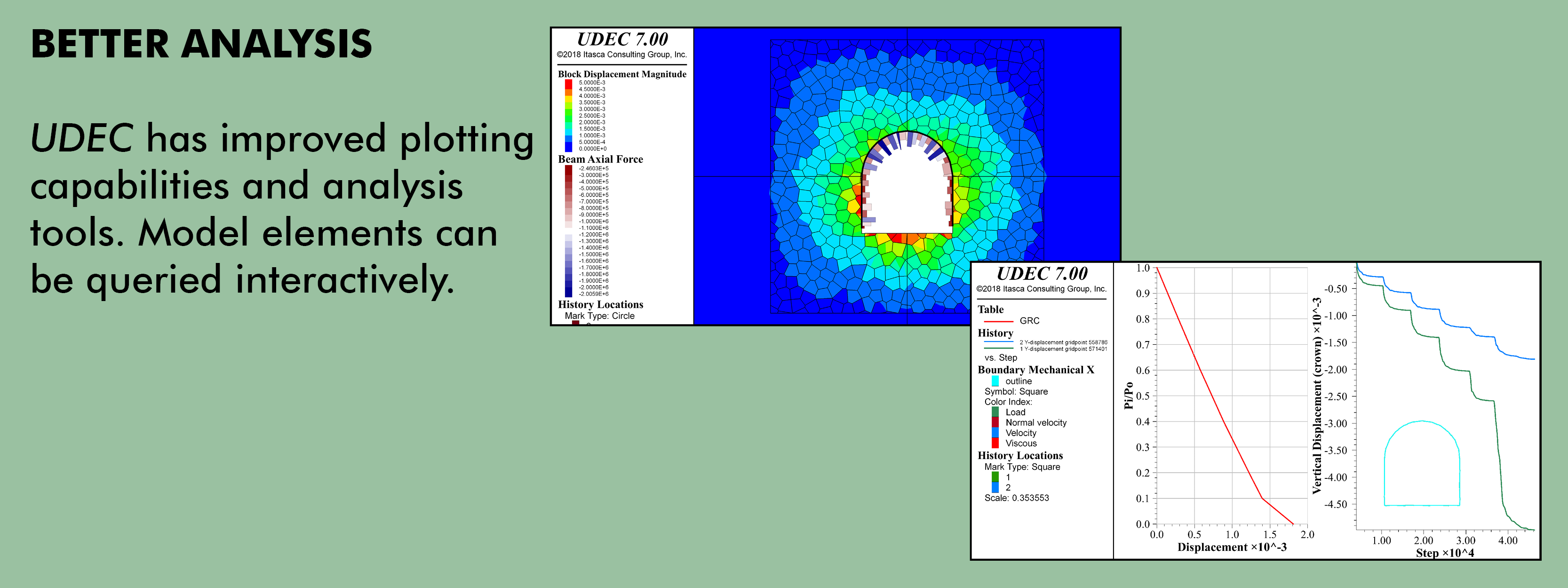
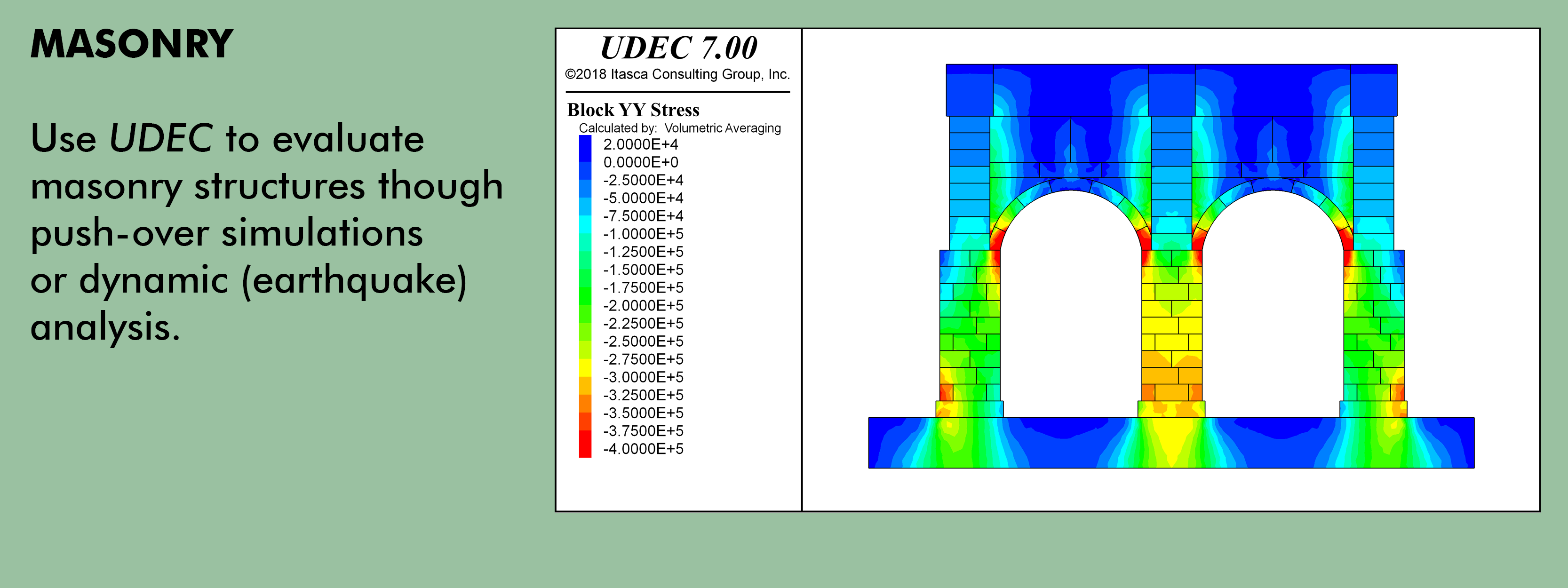
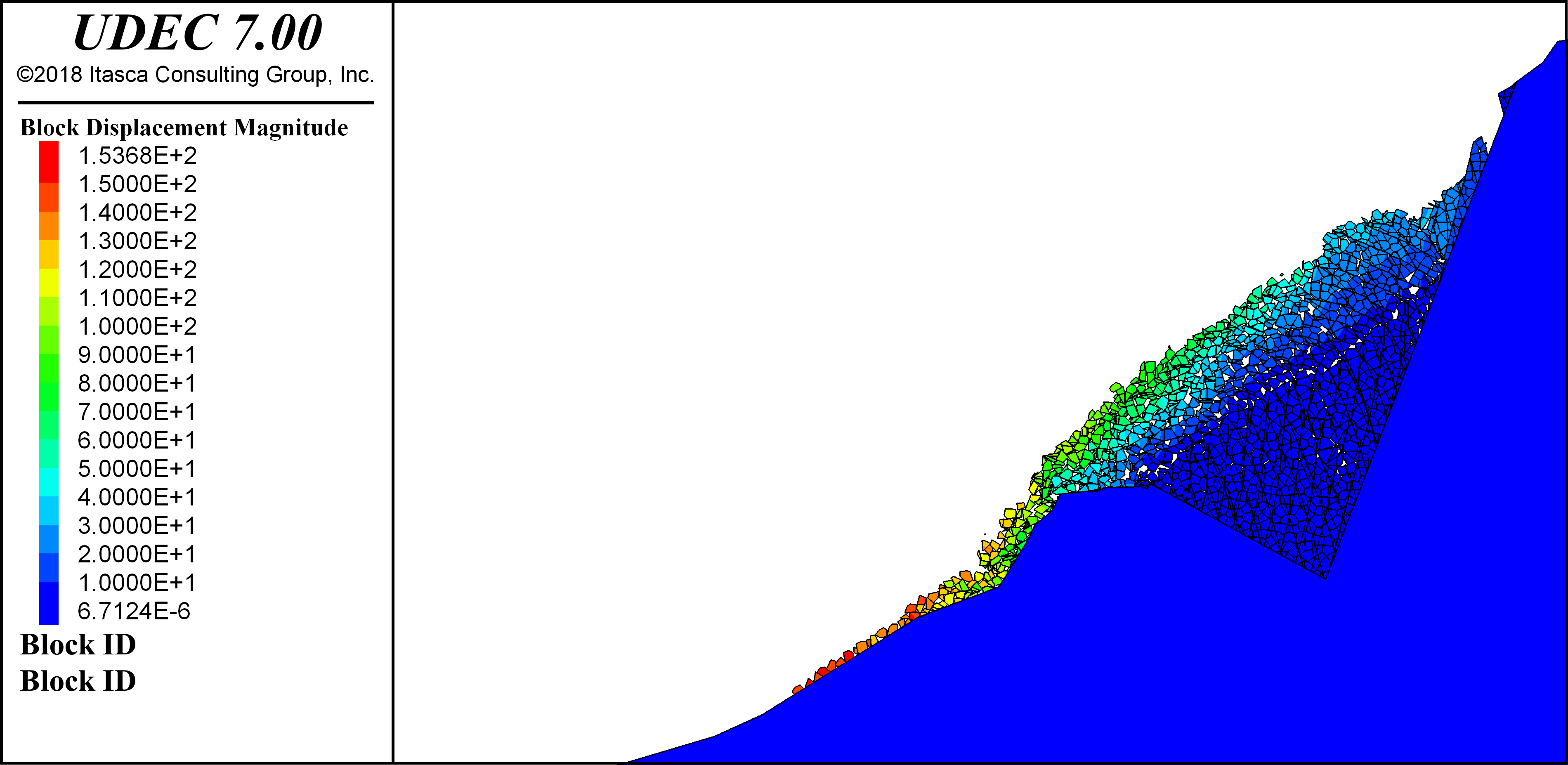
Because UDEC is not limited to a particular type of problem or initial condition, it may be applied to a wide variety of physical behaviors or any case where an understanding of the two-dimensional response of such structures is needed. UDEC is capable of simulating a wide range of engineering and scientific analyzes including: stability analysis of jointed rock slopes or underground excavations; fluid or gas flow through jointed rock; stability of masonry structures, dams, and foundations; blasting, earthquakes, and microseismicity; among many more applications.
Options
Optional features are specialized modules that can be added to UDEC at an additional cost for additional simulation tools.
Fluid Flow: Model fluid flow through the fractures and voids of a system of impermeable blocks. Steady-state pore pressures can be assigned to zones within deformable blocks and boundary conditions may be applied in terms of fluid pressures or defined as an impervious boundary. A porous medium can be defined around the UDEC block model to simulate a regional flow field. Fluid-calculation modes available are: steady-state flow (compressible liquid) and transient flow (compressible liquid, incompressible liquid, compressible gas, and two-phase fluid).
Barton-Bandis Joint Analysis: The Barton-Bandis joint model utilizes a series of empirical relations for joint normal behavior and joint shear behavior based on the effects of surface roughness on discontinuity deformation and strength as described by Barton (1982) and Bandis et al. (1985).
Creep Material Analysis: The creep option can be used to simulate the behavior of materials that time-dependent material behavior.
User-Defined Models (UDM): With this option, users may create their own contact or zone constitutive model for use in UDEC using C++ scripting.
Thermal Analysis: The thermal model simulates the transient flux of heat in materials and the subsequent development of thermally induced stresses. The heat flux is modeled by either isotropic or anisotropic conduction. Heat sources can be added and can be made to decay exponentially with time.